Current Case: Winter 2025
Contributed by: Georgette Dib, MD; Yousef Aldughaythir, MD; Zubeda Sheikh, MBBS, MD, MSCTS, FACNS
Case Report
Clinical presentation: A 32-year-old woman presented with subacute onset of fever, headache, behavioral changes, confusion and myoclonic like movement concerning for seizure activity. On evaluation, she was found to have dysautonomia and orofacial dyskinesias. Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) testing revealed mild lymphocytic pleocytosis, and brain MRI results T2/FLAIR hyperintense signal change in the bilateral temporal lobes and basal leptomeningeal enhancement. She was later found to have an ovarian teratoma.
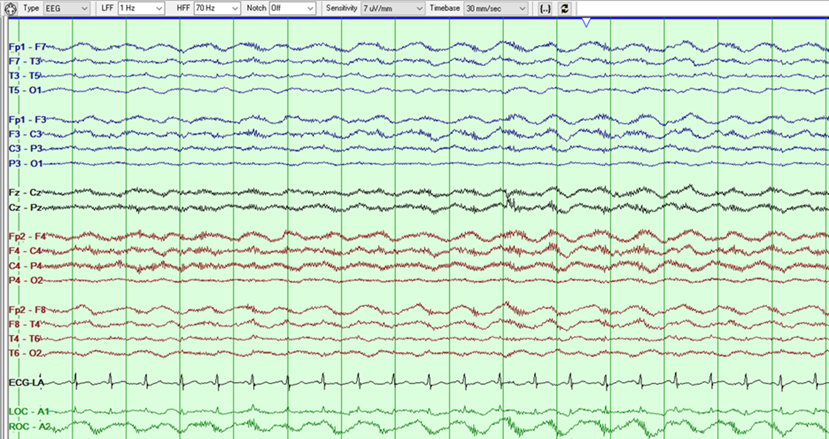
Figure 1: Bipolar Montage
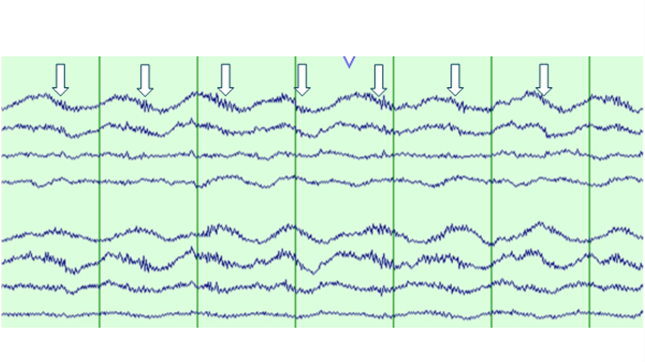
Figure 2: Bipolar Montage
Question 1: What finding is shown in the above EEG clip?
- Periodic discharges with superimposed fast activity (PDs+F)
- Diffuse excess beta activity
- Extreme Delta Brush (EDB)
- Breach rhythm
Answer: (click here)
Correct answer: C. Extreme Delta Brush (EDB)
This figure shows a run of 1Hz frontotemporally predominant generalized rhythmic delta activity (GRDA- frontal) with superimposed fast beta activity that has a stereotyped relationship to the delta waves, occurring maximally on the downstroke of the delta wave as shown below with arrows in a magnified version of the above EEG. Per the 2021 ACNS ICU EEG terminology, extreme Delta Brush is a specific subtype of RDA+F, where there is fast activity cycling with the rhythmic delta and having a stereotyped relationship to the delta wave and occurring on the upstroke, crest or the downstroke of the delta wave (1). It is divided into: Definite EDB: Consists of either abundant or continuous: A. RDA+F, in which the fast activity has a stereotyped relationship to the delta wave (e.g., always maximal on the upstroke, crest, or downstroke of the wave); OR B. PDs+F, in which each PD consists of a single blunt delta wave with superimposed fast activity, and in which the fast activity has a stereotyped relationship to the delta wave (i.e., periodic delta brushes). Possible EDB: Satisfying criterion A) or B) above EXCEPT either: i. only occasional or frequent (rather than abundant or continuous) in prevalence OR ii. the superimposed fast activity lacks a stereotyped relationship to the delta wave; continuous, invariant fast activity during RDA would fall into this category.
Question 2: What clinical conditions are the above EEG findings associated with?
- Anti-DPPX encephalitis
- HSV encephalitis
- Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (anti-NMDAR) encephalitis
- A & C
Answer: (click here)
Correct answer: D. A & C
Anti-NMDAR encephalitis is an autoimmune disease caused by autoantibodies that target cell-surface NMDARs. Anti-NMDAR encephalitis patients typically present with viral prodrome, followed by subacute psychiatric symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, movement abnormalities, and seizures. Previous studies have reported the extreme delta brush, a unique electroencephalography (EEG) pattern, in NMDAR encephalitis patients.(2) EDB is present in only one-third of anti-NMDAR encephalitis patients who have seizures(2,3). EDB was associated overall with increased length of hospital stay, increased ICU admission, and incidence of status epilepticus (4). The etiology of the EDB remains mainly unknown. However, it has been postulated when antibodies block/target the NMDAR, the rhythmic neuronal activity is disrupted, leading to the unique EDB pattern(4). Another theory suggests that delta activity is caused because of focal abnormalities in the brain, and the superimposition of the beta waves is related to the alterations of the NMDA receptors(4). EDB has been recently described in patients with anti-DPPX encephalitis. While extreme delta brushes are not anymore unique to anti-NMDAR encephalitis, its occurrence should trigger testing for autoimmune encephalitis in diagnostically unclear cases(5).
References:
- Hirsch LJ, Fong MWK, Leitinger M, LaRoche SM, Beniczky S, Abend NS, Lee JW, Wusthoff CJ, Hahn CD, Westover MB, Gerard EE, Herman ST, Haider HA, Osman G, Rodriguez-Ruiz A, Maciel CB, Gilmore EJ, Fernandez A, Rosenthal ES, Claassen J, Husain AM, Yoo JY, So EL, Kaplan PW, Nuwer MR, van Putten M, Sutter R, Drislane FW, Trinka E, Gaspard N. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society's Standardized Critical Care EEG Terminology: 2021 Version. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2021 Jan 1;38(1):1-29. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0000000000000806. PMID: 33475321; PMCID: PMC8135051.
- Schmitt SE, Pargeon K, Frechette ES, et al. Extreme delta brush: a unique EEG pattern in adults with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. Neurology 2012;79:1094–100.
- Nathoo, N., Anderson, D., & Jirsch, J. (2021). Extreme Delta Brush in Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis Correlates With Poor Functional Outcome and Death. Frontiers in neurology, 12, 686521. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.686521.
- Parwani J, Ortiz JF, Alli A, Lalwani A, Ruxmohan S, Tamton H, Cuenca VD, Gonzalez D, Anwer F, Eissa-Garcés A, Alzamora IM, Paez M. Understanding Seizures and Prognosis of the Extreme Delta Brush Pattern in Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Encephalitis: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2021 Sep 21;13(9):e18154. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18154. PMID: 34589370; PMCID: PMC8460549.
- Christine Heuer, Leah Disse, Debora Ledergerber, Ilijas Jelcic, Lukas L. Imbach, EEG-Delta brushes in DPPX encephalitis – Welcome to the club, Clinical Neurophysiology Practice, Volume 8, 2023, Pages 12-15, ISSN 2467-981X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnp.2022.11.003.